|
Your score: yourScore correct out of 6 possible assignments.
Correct Answer: The correct assignment of peaks is:
| + | | | | |
|
H3N | | | | |
|  | | | |
| | CHc
−CH2f
−CH2e
−CO−NH
− | CHa
−CO−NH
| −CH2b
−COO - |
|  | |  | |
| OOC | | | CH2d
| |
| | |  | |
| | | SH
| |
Chemical formula for Glutathione
with peaks a to f assigned. |
Protons in -OH, -NH2, SH have no characteristic chemical shift, and their peaks disappear in D2O, as deuterium will replace a proton.
The intensity (area under the peak, not just their height) of peaks 'a' and 'c' appear to be half that of the other peaks, suggesting that peaks 'a' and 'c' likely each correspond to one proton, and the other peaks to two protons.
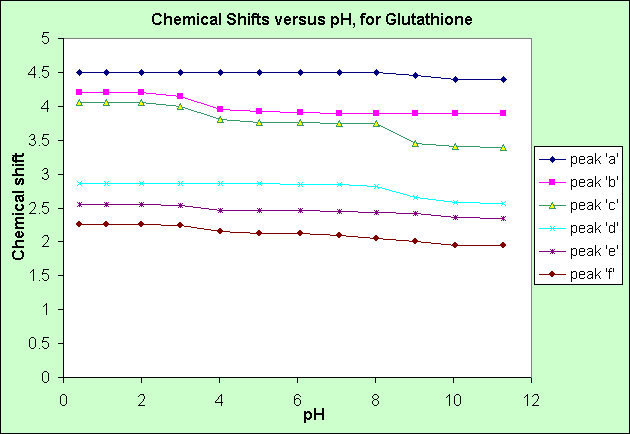
From the above graph of Chemical shift versus pH:
- in alkaline conditions (pH > 7.0): peak 'c' has the greatest chemical shift decrease, followed by peak 'd', then by peaks 'a', 'f' and 'e'.
- in acidic conditions (pH < 7.0): peaks 'b' and 'c' have the greatest shift increase, followed by peaks 'e' and 'f'
- the chemical shifts of peaks 'a' and 'd' do not change in acidic conditions.
An acidic (pH < 7.0) solution donates Hydrogen ions (H+) to, in this case Glutathione, so the COO- groups will accept H+ ions, which will attract electrons from neighbouring groups, hence deshielding these neighbouring groups, increasing their chemical shift. Peaks 'b' and 'c' experience increased chemical shift in acidic conditions, so must be beside the two COO- groups.
Peak 'c' is most affected by reduced chemical shift (increased shielding by electrons) in alkaline conditions, so must be beside the NH2+ group.
Peak ' ? ' is .......
Need to finish this explanation....
Please ask Prof. Homans or a demonstrator about this.
|