| Medical Finals contents: Welcome Finals advice Written exams Clinical revision X-Rays Mock final OSCE's |  |
Medical Finals contents: Monthly quiz PDA's Links Credits Your comments Who are we? |
MCQ's in Rheumatology |
Contributor: Dr. Gary Meenagh January 2006 |

|
Click on the radio-button to the left of the best answer from each of the five possible answers.
A tick mark ![]() will appear if you are right.
will appear if you are right.
A cross mark ![]() will appear if you are wrong.
will appear if you are wrong.
The correct answer will appear in the text-box area below each question.
Your score is updated near the bottom of this page. Only your first answer for each question counts towards your score.
However if your browser does not have javascript, then the answers are at the bottom of this page.
|
(1) A 37 year old female teacher presents with a 2 week history of small joint pain and stiffness in her hands and feet.
Which of the differential diagnoses listed is the least likely explanation for her symptoms? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (c) Fibromyalgia
Inflammatory arthropathies and connective tissue disease can all present in this fashion. In fibromyalgia whilst patients commonly describe 'joint swelling' often this is merely a sensation rather than apparent physical swelling. |
(2) A 67 year old male presents with his first episode of knee pain and swelling together with the following x-ray.
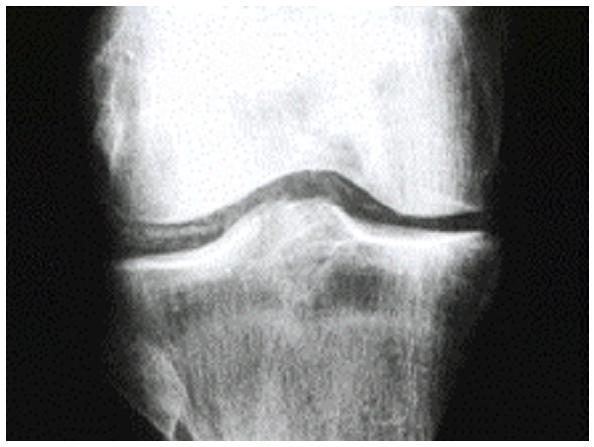 Which of the following investigations is the next investigation indicated diagnostically? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (c) Knee aspiration
The x-ray clearly shows chondrocalcinosis which is meniscal calcification. Whilst this condition can be linked with underlying pathology eg. thyroid disease, haemochromatosis etc., it is imperative to demonstrate the presence of calcium pyrophosphate crystals on plane polarising microscopy. These are classically rhomboid crystals (rather than needle-shaped as found in gout). |
|
(3) A patient with small airway involvement secondary to her rheumatoid disease attends clinic complaining of progressive shortness of breath.
The most clinically relevant parameter on standard pulmonary function testing is: | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (a) High FEF25-75
The earliest finding on pulmonary function testing in patients with small airways involvement in RA is elevation in FEF 25-75. Reduction in DLCO is seen in patients with pulmonary fibrosis which may be due to the condition itself or the treatment (eg. Methotrexate). |
(4) The following pelvic x-ray displays radiographic features of which of the following rheumatic disorders?
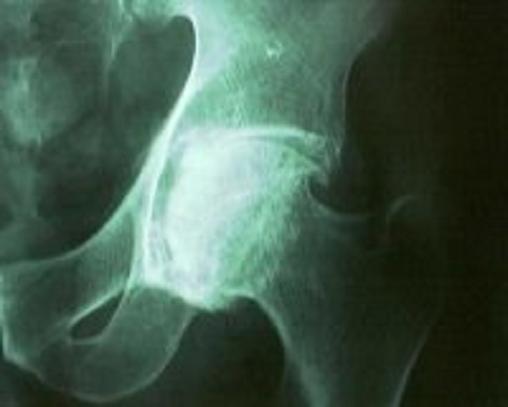 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (d) Osteoarthritis
The x-ray shows medial joint space narrowing, bony sclerosis and marginal osteophytosis - all classical features of osteoarthritis. |
| (5) Which of the following is not included in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) diagnostic criteria for SLE? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (d) Alopecia
Whilst alopecia is a frequent symptom in SLE, it is strangely not included in the ACR criteria for the disease. |
| (6) A disproportionate rise in CRP compared to the ESR is typically found in which of the following clinical situations? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (b) Sepsis in a patient with SLE
A disproportionately high CRP is indicative of sepsis. The ESR and CRP may not reflect the degree of disease activity in some clinical scenarios eg. Psoriatic arthritis and cerebral vasculitis. Often the CRP will rise and fall before the ESR as an inflammatory condition settles. |
| (7) Which of the following types of joint involvement is not seen in psoriatic arthritis? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (b) Jaccoud's arthropathy
Jaccoud's arthropathy is the eponymous name given to the non-erosive arthropathy seen in SLE - typically deforming but non-erosive, and involving the small joints of the hands. |
| (8) In septic arthritis which one of the following pairings is most commonly found in hospital practice? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (d) Knee joint and Staph Aureus
The knee joint is the commonest joint to be involved in a septic episode and the most common organism is Staphylococcus. |
| (9) Which of the following is not a recognised risk factor for osteoporosis? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (a) Early menarche
Any condition which leads to a shortening of the exposure to oestrogens will increase risk of developing osteoporosis. A late onset of menarche will therefore be more relevant than an early one. |
| (10) All of the following are rheumatic manifestations of malignancy with the exception of which one? | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Answer will appear here after you select an option above.
Answer: (c) Degenerative joint change
Degenerative arthropathy is not linked with an underlying malignancy. Gout is common in patients with a lymphoproliferative state. Dermatomyosistis and cryoglobulinaemia can be associated with malignancy in a proportion of patients and should always be excluded when a patient presents with these diagnoses. HPOA is often diagnosed coincidentally when patients have a hand and wrist x-ray for an 'arthritic complaint'. |
PLEASE give us some feedback, using the comments form about what you think of the questions (relevance, level of difficulty, what you would like to see more of etc.), so that we can further update the site appropriately. Thankyou.
| Question number | Answers are: |
|---|---|
| (1) | (c) Fibromyalgia Inflammatory arthropathies and connective tissue disease can all present in this fashion. In fibromyalgia whilst patients commonly describe 'joint swelling' often this is merely a sensation rather than apparent physical swelling. |
| (2) | (c) Knee aspiration The x-ray clearly shows chondrocalcinosis which is meniscal calcification. Whilst this condition can be linked with underlying pathology eg. thyroid disease, haemochromatosis etc., it is imperative to demonstrate the presence of calcium pyrophosphate crystals on plane polarising microscopy. These are classically rhomboid crystals (rather than needle-shaped as found in gout). |
| (3) | (a) High FEF25-75 The earliest finding on pulmonary function testing in patients with small airways involvement in RA is elevation in FEF 25-75. Reduction in DLCO is seen in patients with pulmonary fibrosis which may be due to the condition itself or the treatment (eg. Methotrexate). |
| (4) | (d) Osteoarthritis The x-ray shows medial joint space narrowing, bony sclerosis and marginal osteophytosis - all classical features of osteoarthritis. |
| (5) | (d) Alopecia Whilst alopecia is a frequent symptom in SLE, it is strangely not included in the ACR criteria for the disease. |
| (6) | (b) Sepsis in a patient with SLE A disproportionately high CRP is indicative of sepsis. The ESR and CRP may not reflect the degree of disease activity in some clinical scenarios eg. Psoriatic arthritis and cerebral vasculitis. Often the CRP will rise and fall before the ESR as an inflammatory condition settles. |
| (7) | (b) Jaccoud's arthropathy Jaccoud's arthropathy is the eponymous name given to the non-erosive arthropathy seen in SLE - typically deforming but non-erosive, and involving the small joints of the hands. |
| (8) | (d) Knee joint and Staph Aureus The knee joint is the commonest joint to be involved in a septic episode and the most common organism is Staphylococcus. |
| (9) | (a) Early menarche Any condition which leads to a shortening of the exposure to oestrogens will increase risk of developing osteoporosis. A late onset of menarche will therefore be more relevant than an early one. |
| (10) | (c) Degenerative joint change Degenerative arthropathy is not linked with an underlying malignancy. Gout is common in patients with a lymphoproliferative state. Dermatomyosistis and cryoglobulinaemia can be associated with malignancy in a proportion of patients and should always be excluded when a patient presents with these diagnoses. HPOA is often diagnosed coincidentally when patients have a hand and wrist x-ray for an 'arthritic complaint'. |