| Medical Finals contents: Welcome Finals advice Written exams Clinical revision X-Rays Mock final OSCE's |  |
Medical Finals contents: Monthly quiz PDA's Links Credits Your comments Who are we? |
Question 1 | |||||
A 45 year old man presents after an episode of haematemesis, and is clinically anaemic (see picture below).
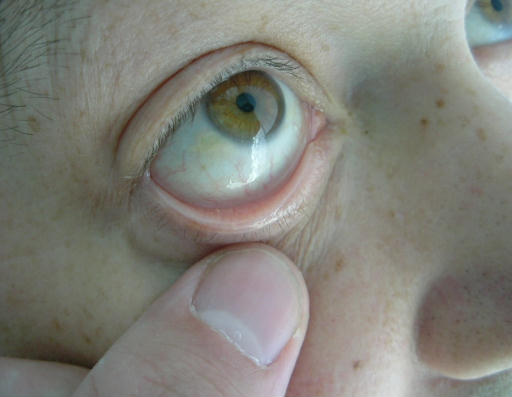 Which of the following factors is not important when predicting his chance of mortality? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (e) Previous haematemesis
The Rockall score can be calculated in cases of gastrointestinal tract bleeding to give an estimate of mortality risk. The factors influencing the score are:
A score of 0 is associated with a mortality of 0.2%, whereas a score of 6 is associated with 49% mortality. Further details can be found here: http://www.bsg.org.uk/bsgjava/rockall.html |
Question 2 | |||||
|
A 37 year old female complains of fatigue and right upper quadrant abdominal discomfort. She is found to have high circulating levels of anti-nuclear antibodies and anti-smooth muscle antibodies.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (b) Autoimmune hepatitis
These presenting symptoms are vague, but are typical of patients with this condition. Autoimmune hepatitis is commoner in women than men, and may be associated with other autoimmune conditions. Anti-nuclear, anti-smooth muscle and anti-liver/kidney microsomal 1 antibodies are typically associated with this condition, and increased levels of globulins are characteristic. Treatment is with immunosuppression. Cessation of therapy can be considered when the patient is asymptomatic, when bilirubin and liver enzymes are normal or near normal, when gamma globulin levels are normal and when a biopsy specimen is found to be normal or near-normal. |
Question 3 | |||||
|
You review a patient with haemochromatosis at a clinic. He asks you about the potential complications of the condition.
Which of the following options is not a common complication? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (c) Pulmonary fibrosis
Haemochromatosis results from a genetic mutation in the HFE gene that controls iron transport in the gut. It is characterised by iron overload. Iron deposition in various organs produces the clinical manifestations and complications of the disease:
|
Question 4 | |||||
| Which of the following drugs can cause oesophagitis? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (e) Potassium
Drugs commonly linked with oesophagitis include:
|
Question 5 | |||||
| Which of the following cancers is not commoner in patients with coeliac disease? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (b) Small cell lung cancer
All the other cancers mentioned may occur more commonly in patients with coeliac disease. However, the risk associated with these cancers is no greater than that of the general population if patients adhere to a gluten-free diet. |