| Medical Finals contents: Welcome Finals advice Written exams Clinical revision X-Rays Mock final OSCE's |  |
Medical Finals contents: Monthly quiz PDA's Links Credits Your comments Who are we? |
This 65 year-old retired bus driver presented to hospital with shortness of breath and haemoptysis. He also complained of tender wrists bilaterally.
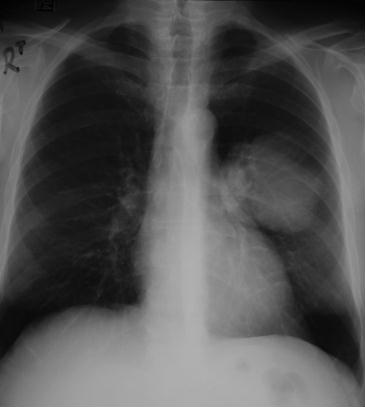 What do you think is the most likely cause for his painful wrists? |
| (a) Inflammatory arthritis |
| (b) Pathological wrist fractures |
| (c) Osteomyelitis |
| (d) Malignant infiltration of the brachial pleuxus |
| (e) Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPOA) - THE CORRECT ANSWER |
(e) Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPOA)
Chest X-ray Report:
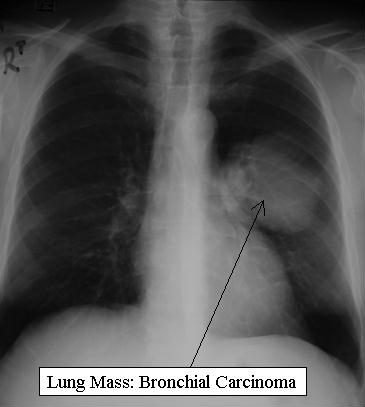 This is a PA Chest X-ray of an adult male patient. A large well circumscribed mass of soft tissue density is seen within the left lung. No central cavitation is seen. No bony or pulmonary metastatic disease is noted. HPOA is associated with malignancy and lung abscess. Associated malignancies include: bronchial carcinoma, metastatic disease and lymphoma. |
Treeton Hospital's medical SHO performed a pleural aspiration on the 50 year-old women whose chest x-ray is shown below.
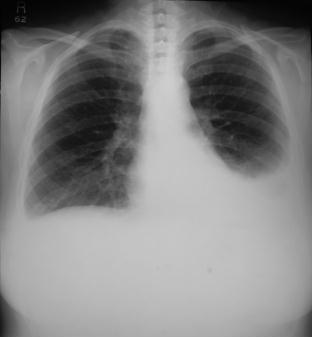
What is the most likely cause of the effusion from your interpretation? |
| (a) Bronchial carcinoma |
| (b) Hypothyroidism - THE CORRECT ANSWER |
| (c) Pneumonia |
| (d) Rheumatoid disease |
| (e) Pulmonary embolus |
|
(b) Hypothyroidism
Pleural effusions are divided into exudates and transudates. This is based on the total protein content of pleural fluid. Exudate = greater than 30 g/l of protein
Exudates tend to be unilateral and trasudates bilateral due to the nature of the causative factors. 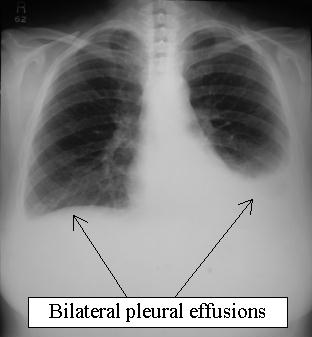 The CXR shows bilateral pleural effusions - albeit larger on the left. The aspirate analysis also shows a transudate. The only option within the list which causes a transudate is hypothyroidism. |
This 45 year-old women was admitted with abdominal pain and became short of breath. CT chest was performed.
 What abnormality is seen on the CT scan? |
| (a) Bilateral pneumonia |
| (b) Bilateral pleural thickening |
| (c) A pulmonary nodule |
| (d) Bilateral pleural effusions - THE CORRECT ANSWER |
| (e) Bilateral sub-phrenic abscesses |
|
D. Bilateral pleural effusions
Acute pancreatitis is a common cause of abdominal pain and associated with the development of pleural effusions. Gallstones and alcohol are the most common causes of pancreatitis. Pleural aspiration of an effusion can be undertaken and analyzed for amylase. 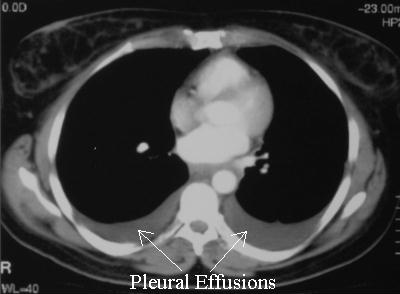 |
|
Whilst acting as a medical volunteer for the St John's Ambulance at a local fete a 21 year-old lady is brought to you with grossly swollen lips, face and wheeze following a bee sting. He is finding it difficult to breath and his BP is 83/45 from a manual reading,
What should be done next? |
| (a) Give 1:1000 IV adrenaline + IV hydrocortisone |
| (b) Observe and arrange transfer to casualty |
| (c) Give IV hydrocortisone |
| (d) Give 1:1000 IM adrenaline + IV hydrocortisone - THE CORRECT ANSWER |
| (e) Give 1:10,000 IV adrenaline + IV hydrocortisone |
|
(d) Give 1:1000 IM adrenaline + IV hydrocortisone
Anaphylaxis requires immediate treatment. Those with known anaphylactic reactions (often to a specific substance such as peanuts) carry their own treatment in the form of a preloaded syringe of adrenaline. When the symptoms are mild and vital signs are within normal range the administration of IV hydrocortisone and chlorpheniramine is sufficient. Adrenaline being available should symptoms before more profound. If circulatory failure develops (SHOCK) adrenaline should be administered. This takes the form of 1:1000 adrenaline given via the intramuscular (IM) route. Note this is different to during cardiac arrest when it is 1:10,000 via an intravenous (IV) route. Hydrocortisone, even by intravenous route, takes several hours to have an effect. It is the inotropic action of adrenaline which gives an immediate response. It is also appropriate if anaphylactic shock occurs to give IV fluids to maintain the circulatory volume. |
A 26 year-old student takes a household substance in excess during a suicide attempt
What is the patient's anion gap? |
| (a) 26.3 - THE CORRECT ANSWER |
| (b) 21.3 |
| (c) 23.1 |
| (d) 47.7 |
| (e) 2.13 |
|
This deliberate overdose has caused a metabolic acidosis. One should always calculate the anion gap when a metabolic acidosis is observed. If the anion-gap is increased it is due to the presence of an exogenous acid or acid present in unmeasured small quantities during health. This is calculated by subtracting the main anions (negative charge) in the plasma, bicarbonate and chloride, from the main cations (positive charge), sodium and potassium. The anion gap is usually composed of negatively charged proteins, organic acids and phosphate.
|
The winner of the free ticket to The 1st Belfast SCRUBS Undergraduate Trauma & Acute Medicine Conference will be picked at random from all entries.
We will contact the winner via email.