| Medical Finals contents: Welcome Finals advice Written exams Clinical revision X-Rays Mock final OSCE's |  |
Medical Finals contents: Monthly quiz PDA's Links Credits Your comments Who are we? |
Question 1 | |||||
|
A 54 year-old woman is admitted with right loin pain and haematuria. Tenderness in the right loin is found on examination.
A computed tomography scan of kidneys, ureters and bladder (CT-KUB) is performed (see below). A right renal tract calculus is observed. 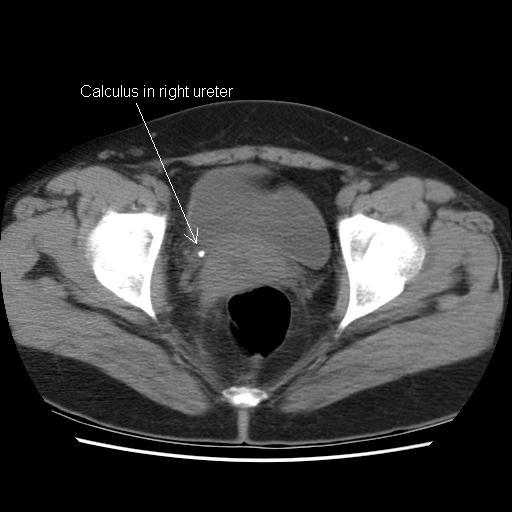 What is the most common location for renal tract calculi? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (c) Vesicoureteric junction
CT-KUB is the first line imaging modality in most centres for patients with renal colic, although intravenous urography (IVU) is still used in some hospitals. A plain abdominal radiograph is of limited use in acute renal colic, but may be used to monitor a known radio-opaque calculus. Renal calculi come in various types (see box)
The 3 most common locations for renal calculi (from proximal to distal) within the renal tract are:
|
Question 2 | |||||
|
A patient has been treated with various drugs including gold injections for joint disease. She has now developed bronchiectasis.
Which of the following blood results would be in keeping with this information? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (a) Low immunoglobulins
Some drugs including gold can cause an acquired immunodeficiency leading to low levels of immunoglobulins. This in turns predisposes to repeated infections. Recurrent respiratory tract infections can eventually lead to scarring and dilatation of distal airways. This eventually causes them to fill with mucous which subsequently becomes infected - this is bronchiectasis.
Bence Jones protein is a urine test useful in the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Anti-double stranded DNA antibody is a very specific test for systemic lupus erythematosus. Anti-nuclear antibody is positive in several immunological conditions. |
Question 3 | |||||
The clinician looking after a 73 year-old man with newly diagnosed iron deficiency anaemia is worried about the part of the bowel shown in this barium enema.
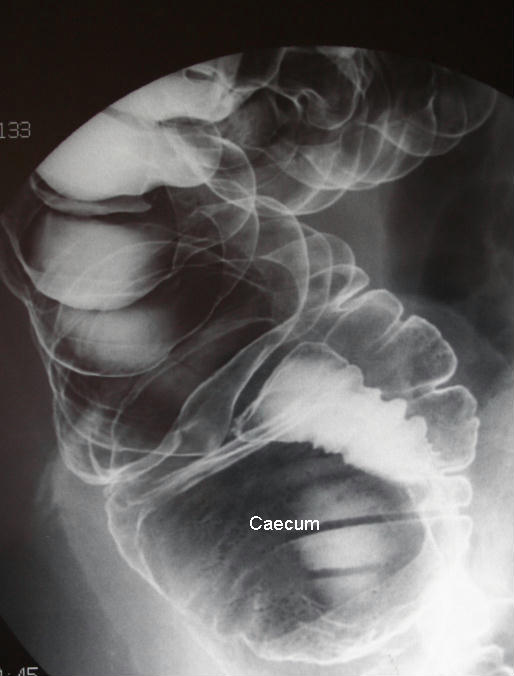 What diagnosis is he most worried about? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (d) Caecal carcinoma
Colorectal malignancy is one of the commonest malignancies in the UK population. In terms of presentation they can be divided into LEFT and RIGHT sided tumours. The presenting symptoms differ, with some overlap, as shown in the boxes.
On a barium enema, caecal carcinoma is observed as a filling defect within the bowel (the barium contrast being unable to fill the luminal part of the caecum occupied by the tumour mass). The commonest part of the large bowel to be affected by Crohn's disease is the ileo-caecal segment. | |||||
Question 4 | |||||
|
A 46 year-old solicitor complains of right upper quadrant pain and has deranged liver function tests. An ultrasound scan of the abdomen demonstrated a dilated common bile duct. He proceeds to endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography (ERCP).
Whilst observing the procedure, the consultant in charge asks you the location of the Ampulla of Vater. Where does the ampulla of Vater enter the bowel? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (c) Descending (second part) duodenum
The small intestine is composed of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The duodenum is divided into 4 parts: ascending, descending, inferior and superior. The duodenum is C-shaped the first part often being referred to as the duodenal cap. The confluence of the common bile duct and pancreatic duct enters the descending (second part) of the duodenum as the Ampulla of Vater (major duodenal papilla). The side viewing aspect of the ERCP endoscope is used to cannulate the Ampulla of Vater allowing access to the biliary tree. |
Question 5 | |||||
|
A patient with inflammatory arthritis develops an acutely swollen, painful hot elbow 2 days following an intra-articular steroid injection.
What is the most appropriate initial course of action? | |||||
| |||||
|
Answer: (a) Blood cultures, repeat joint aspiration and intravenous antibiotics
Introducing infection is a serious complication of intra-articular steroid injection. This is why it is very important to use aseptic technique. Septic arthritis needs prompt treatment with intravenous antibiotics to reduce long term damage to the joint. |